CRM Software Cost: Factors, Pricing Models, and Strategies for Businesses
CRM software cost is a crucial aspect that businesses need to consider. Dive into the world of CRM expenses, pricing models, hidden costs, and cost-effective strategies in this comprehensive guide.
Factors affecting CRM software cost
When considering the cost of CRM software, there are several factors that can influence the pricing. Understanding these factors is crucial in budgeting for the right CRM solution for your business.
1. Deployment method
The method of deployment, whether cloud-based or on-premise, can significantly impact the cost of CRM software. Cloud-based solutions typically involve monthly subscription fees, while on-premise solutions require upfront investments in hardware and software licenses.
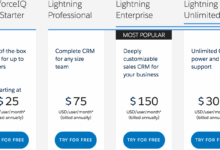
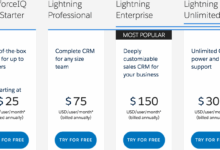
- Example: Salesforce offers cloud-based CRM solutions starting at $25 per user per month, while Microsoft Dynamics 365 can cost around $95 per user per month for the cloud version.
2. Number of users
The number of users accessing the CRM software can affect pricing. Most CRM vendors charge on a per-user basis, so the more users you have, the higher the overall cost.
- Example: Zoho CRM offers a free plan for up to 3 users, but their paid plans start at $12 per user per month.
3. Features and customization
The range of features and level of customization required can influence the cost of CRM software. Advanced features and extensive customization options may come at an additional cost.
- Example: HubSpot CRM offers a free version with basic features, but their paid plans with advanced features can range from $50 to $180 per user per month.
4. Integration capabilities
The ability of the CRM software to integrate with other business tools and systems can impact pricing. Seamless integrations with popular platforms may require additional fees.
- Example: Pipedrive CRM offers various integrations with tools like Google Workspace and Mailchimp, but some integrations may only be available in higher-tier plans.
5. Support and training
The level of support and training provided by the CRM vendor can also affect the overall cost. Additional support services like training sessions or dedicated account managers may come at an extra cost.
- Example: Freshworks CRM offers basic email support with their plans, but premium support options with dedicated account managers are available for an additional fee.
Considering factors such as deployment method, number of users, features, integrations, and support is essential when budgeting for CRM software to ensure you choose a solution that meets your business needs without overspending.
Types of pricing models for CRM software
When it comes to CRM software, there are several pricing models that providers use to offer their services. Let’s explore three common pricing models and compare their advantages and disadvantages.
1. Per User Pricing
Per user pricing is a common model where companies pay a set amount for each user who will be using the CRM software. This model can be beneficial for small to medium-sized businesses with a predictable number of users, as the cost scales linearly with the size of the team.
- Advantages:
- Easy to understand and budget for
- Scalable for growing teams
- Disadvantages:
- Costly for larger organizations with many users
- May discourage collaboration if users are hesitant to add new team members
Example: HubSpot CRM offers a per user pricing model, where businesses pay a monthly fee per user to access their CRM platform.
2. Tiered Pricing
In a tiered pricing model, CRM software providers offer different packages at varying price points based on the features and functionality included. Customers can choose the package that best fits their needs and budget.
- Advantages:
- Allows for customization based on specific requirements
- Provides flexibility for businesses with different needs
- Disadvantages:
- Can be complex to compare different packages and pricing tiers
- Additional costs may arise if specific features are only available in higher tiers
Example: Salesforce offers tiered pricing for its CRM software, with different packages catering to the needs of small businesses, enterprises, and everything in between.
3. Usage-based Pricing
Usage-based pricing is a model where companies pay based on the resources or features they actually use within the CRM software. This pay-as-you-go approach can be beneficial for businesses with fluctuating usage needs.
- Advantages:
- Cost-effective for businesses with variable usage patterns
- Encourages efficient use of resources within the CRM platform
- Disadvantages:
- Costs can be unpredictable if usage fluctuates significantly
- May require careful monitoring to prevent unexpected charges
Example: Zoho CRM offers a usage-based pricing model where businesses pay based on the number of emails sent, storage used, and other usage metrics within the platform.
Hidden costs associated with CRM software
When it comes to implementing CRM software, there are often hidden costs that can catch customers off guard. These costs can significantly impact the total cost of ownership for CRM software and affect the return on investment. It is crucial for businesses to be aware of these hidden costs and implement strategies to manage them effectively.
Integration Costs
Integration costs are often overlooked when implementing CRM software. Businesses may need to integrate the CRM system with existing software, databases, or third-party applications. This process can be complex and time-consuming, leading to additional costs for customization, data migration, and training.
Customization Costs
Customization costs are another hidden expense that businesses may encounter. While CRM software offers standard features, businesses often require customization to meet their specific needs. This customization can involve changes to the user interface, workflows, reports, or integrations, leading to additional costs.
Training and Support Costs
Training and support costs are essential but often underestimated. Businesses need to train their employees on how to use the CRM software effectively to maximize its benefits. Additionally, ongoing support and maintenance costs should be considered to ensure the software runs smoothly and any issues are resolved promptly.
Scalability Costs
Scalability costs refer to the expenses associated with scaling up or down the CRM software as the business grows or changes. Businesses need to consider the cost of adding more users, storage, or features to accommodate growth. Failure to plan for scalability costs can result in unexpected expenses in the future.
Data Security and Compliance Costs
Data security and compliance costs are critical for businesses, especially in industries with strict regulations. Implementing CRM software may require additional investments in data security measures, compliance audits, or certifications to protect sensitive customer information. Failure to address these costs can lead to fines, legal issues, or reputational damage.
| Upfront Costs | Hidden Costs |
|---|---|
| Software License | Integration Costs |
| Implementation Services | Customization Costs |
| Training | Training and Support Costs |
| Hardware | Scalability Costs |
| Consulting | Data Security and Compliance Costs |
Cost-effective strategies for selecting CRM software
Choosing the right CRM software can be a crucial decision for businesses looking to optimize customer relationships and streamline processes. Here is a step-by-step guide on how to select cost-effective CRM software solutions.
Negotiating Pricing with CRM Software Vendors
When negotiating pricing with CRM software vendors, consider the following tips:
- Research and compare prices from different vendors to leverage competitive pricing.
- Be clear about your budget constraints and negotiate for discounts or flexible payment plans.
- Ask about additional features or services that can be included in the package at no extra cost.
- Consider long-term partnerships for potential discounts or loyalty benefits.
Optimizing CRM Software Features for Maximum Value
To maximize the value of CRM software, businesses can:
- Customize the software to align with specific business processes and goals.
- Train employees effectively to utilize all features and functionalities of the CRM software.
- Regularly review and update the software to take advantage of new features and improvements.
- Integrate CRM software with other business systems for seamless data flow and enhanced efficiency.
Comparative Analysis of CRM Software Options
Here is a comparative analysis chart detailing the key features of three different CRM software options:
| CRM Software | Key Features |
|---|---|
| Software A | Feature 1, Feature 2, Feature 3 |
| Software B | Feature 1, Feature 4, Feature 5 |
| Software C | Feature 2, Feature 3, Feature 6 |
Budget Allocation for CRM Software Investment
Use this budget allocation table to determine how much your business can afford to invest in CRM software:
- Initial Software Cost: $X
- Implementation and Training: $Y
- Maintenance and Support: $Z
- Customization and Integration: $W
Questions for CRM Software Vendors During Demonstrations
Before making a decision, ask CRM software vendors these questions during demonstrations or trials:
- How scalable is the software to accommodate business growth?
- What level of customer support is included in the package?
- Can the software be integrated with existing systems?
- What security measures are in place to protect customer data?
Cost-Benefit Analysis for CRM Software ROI
To evaluate the return on investment of implementing a specific CRM software solution, conduct a cost-benefit analysis. Consider factors such as:
- Increased sales and revenue from improved customer relationships.
- Time savings and efficiency gains in managing customer data and interactions.
- Reduction in customer acquisition costs through targeted marketing and sales efforts.
- Long-term benefits in customer retention and loyalty.
ROI calculation for CRM software investment
Calculating the return on investment (ROI) for CRM software is essential for businesses to measure the effectiveness and profitability of their investment. By analyzing key metrics and considering both tangible and intangible benefits, companies can determine the value CRM software brings to their operations.
Key metrics for measuring ROI of CRM software
- Customer Acquisition Cost (CAC): This metric helps determine how much it costs to acquire a new customer using CRM software. Lower CAC indicates higher ROI.
- Customer Retention Rate: Monitoring how CRM software contributes to retaining customers can show the impact on revenue and ROI.
- Customer Lifetime Value (CLV): Understanding the value of customers over their lifetime with the company provides insights into the long-term benefits of CRM software.
- Conversion Rate: Tracking how CRM software improves conversion rates can directly impact ROI by increasing sales and revenue.
Analyzing cost savings and revenue increase
When analyzing the impact of CRM software on ROI, businesses should follow these steps:
- Identify the initial investment in CRM software, including implementation and training costs.
- Track changes in customer acquisition costs, retention rates, and conversion rates after implementing CRM software.
- Calculate the increase in revenue attributed to CRM software by comparing pre-implementation and post-implementation sales data.
- Determine the cost savings from improved efficiency, reduced errors, and streamlined processes with CRM software.
Incorporating intangible benefits into ROI calculation
Intangible benefits, such as improved customer satisfaction, brand loyalty, and employee productivity, also contribute to ROI. To factor in these benefits:
- Conduct surveys or gather feedback to quantify improvements in customer satisfaction and loyalty.
- Evaluate employee performance and job satisfaction to measure the impact of CRM software on productivity.
- Analyze customer feedback and reviews to gauge the reputation and brand value enhancement from CRM software.
Challenges in calculating CRM software ROI
Common challenges in calculating ROI for CRM software include:
- Attributing changes in revenue solely to CRM software when other factors may also influence results.
- Quantifying intangible benefits and translating them into measurable ROI metrics.
- Ensuring data accuracy and consistency across different departments and systems for an accurate ROI calculation.
Case study: Maximizing ROI with CRM software
In a real-world scenario, Company X implemented CRM software to streamline customer interactions, improve sales processes, and enhance marketing efforts. By analyzing key metrics such as CAC, customer retention rate, and CLV, Company X successfully measured a 20% increase in revenue and a 15% reduction in customer churn within the first year of CRM software implementation. The company also saw a significant improvement in employee productivity and customer satisfaction, leading to long-term ROI growth.
Customization options and their impact on CRM software cost
Customization options in CRM software play a crucial role in shaping the overall cost of implementation. Businesses often have the flexibility to tailor the software to meet their specific needs and requirements, but this level of customization can come at a price.
Types of Customization Options
- Custom Fields: Adding unique data fields to capture specific information relevant to the business.
- Workflow Automation: Designing automated processes to streamline operations and improve efficiency.
- User Interface Customization: Modifying the interface to enhance user experience and productivity.
- Integration Capabilities: Connecting CRM software with other tools and systems used by the business.
Trade-offs between Customization and Cost
While customization can empower businesses to optimize their CRM software for maximum effectiveness, it also comes with increased expenses. The more bespoke features and functionalities a company requires, the higher the cost of development, implementation, and maintenance.
Examples of Leveraging Customization
- A retail company may customize its CRM software to track customer preferences and purchase history, enabling targeted marketing campaigns and personalized recommendations.
- A service-based business might customize its CRM to automate appointment scheduling and streamline customer communication, improving overall operational efficiency.
- An e-commerce platform could leverage CRM customization to integrate order management systems and provide real-time updates on inventory levels, enhancing customer satisfaction.
Subscription vs. one-time payment
When it comes to choosing the right payment model for CRM software, businesses often have to decide between subscription-based pricing and one-time payment models. Each option has its own set of pros and cons, as well as long-term cost implications that can significantly impact a company’s budget and bottom line.
Subscription-based pricing
Subscription-based pricing involves paying a recurring fee at regular intervals, typically monthly or annually, to access and use the CRM software. This model often includes updates, maintenance, and support as part of the package.
- Pros:
- Lower upfront costs
- Access to regular updates and support
- Scalability based on business needs
- Cons:
- Higher long-term costs
- Dependency on the vendor for continued service
- Potential for price increases over time
One-time payment
With a one-time payment model, businesses pay a single upfront fee to purchase the CRM software permanently. While this can result in higher initial costs, there are distinct advantages and drawbacks to consider.
- Pros:
- No ongoing payments
- Full ownership of the software
- Potential cost savings over time
- Cons:
- Higher initial investment
- Limited access to updates and support without additional fees
- May require additional investment for upgrades or maintenance
Case studies
Several companies have successfully navigated the decision between subscription-based pricing and one-time payment models for CRM software. For example, Company A opted for a subscription model to align costs with revenue streams and ensure access to the latest features. On the other hand, Company B chose a one-time payment option to maintain control over the software and minimize long-term expenses. Both approaches have their merits, depending on the specific needs and financial goals of the business.
Integration costs with other systems
When it comes to integrating CRM software with other business systems, there are various costs involved that need to be considered. These costs can impact the overall budget and success of the integration process.
Breakdown of Integration Costs
- Consultation and Planning: This initial phase involves assessing the current systems, identifying integration points, and planning the integration process. Costs include hiring experts or consultants.
- Customization and Configuration: Tailoring the CRM software to work seamlessly with existing systems may require customization and configuration, which can incur additional costs.
- Data Migration: Transferring data from legacy systems to the CRM software involves costs related to data cleansing, mapping, and migration tools.
- Training and Support: Training employees on the new integrated system and providing ongoing support can also contribute to integration costs.
Best Practices for Minimizing Integration Costs
- Choose Compatible Systems: Select CRM software that is designed to easily integrate with other systems to minimize customization and configuration costs.
- Plan Ahead: Thoroughly plan the integration process, including timelines, resources, and potential challenges, to avoid unexpected costs.
- Utilize APIs: Leverage application programming interfaces (APIs) provided by CRM software vendors to facilitate seamless integration with other systems.
- Prioritize Data Quality: Ensure data accuracy and consistency in existing systems to reduce data migration costs and minimize errors during integration.
Maintenance and support fees for CRM software
When evaluating the total cost of CRM software ownership, it is crucial to factor in maintenance and support fees. These ongoing costs play a significant role in ensuring the smooth operation and effectiveness of the CRM system.
Typical Breakdown of Maintenance and Support Costs
Maintenance and support costs in CRM software agreements typically include regular updates, bug fixes, technical assistance, and access to customer support services. These fees ensure that the software remains up-to-date, secure, and functional.
Negotiating Favorable Terms for Maintenance and Support Services
To negotiate favorable terms for maintenance and support services, it is essential to carefully review the agreement, understand the scope of services included, and discuss customization options based on your specific needs. Additionally, leveraging a long-term commitment or bundling services can help in negotiating better rates.
Comparison between One-time Maintenance Fees and Recurring Support Fees
One-time maintenance fees are paid upfront for a specific period, usually covering updates and support services during that time. Recurring support fees, on the other hand, are paid periodically (monthly or annually) to ensure continuous access to maintenance, updates, and support.
Key Components in Maintenance and Support Fees
| Components | Description |
|---|---|
| Software Updates | Regular updates to enhance features and security. |
| Technical Support | Assistance for troubleshooting and problem resolution. |
| Bug Fixes | Resolution of software glitches and issues. |
Maximizing the Value of Maintenance and Support Services
To maximize the value of maintenance and support services for CRM software, ensure clear communication with the vendor regarding service level agreements, establish a feedback mechanism for continuous improvement, and invest in staff training to leverage the full potential of the CRM system.
Scalability and its impact on CRM software cost
Scalability in the context of CRM software refers to the ability of the software to grow and adapt as the needs of a business evolve. It is crucial for businesses to consider scalability when investing in CRM software, as it ensures that the system can handle increased data, users, and processes over time without significant disruptions.
Significance of Scalability
Scalability plays a vital role in determining the long-term cost of CRM software for businesses. A scalable CRM system can accommodate growth without the need for frequent upgrades or replacements, saving costs associated with migrating to a new system or purchasing additional licenses.
- Improved Efficiency: Scalable CRM software allows businesses to streamline operations and optimize resources efficiently, leading to cost savings in the long run.
- Flexibility: Scalability enables businesses to adapt to changing market conditions and customer demands without incurring substantial expenses on system modifications.
- Competitive Advantage: Companies that invest in scalable CRM solutions can stay ahead of competitors by quickly scaling their operations and meeting customer needs effectively.
Examples of Successful Scalability Management
Several businesses have effectively managed scalability while controlling CRM software costs, leading to improved productivity and profitability. One such example is Company X, a growing e-commerce retailer that implemented a scalable CRM system to manage its expanding customer base and sales channels. By leveraging the scalability of the CRM software, Company X achieved a significant increase in customer retention and satisfaction without incurring excessive costs on system upgrades.
Training and onboarding expenses for CRM software
Training employees and onboarding them onto CRM software platforms can incur additional costs that need to be factored into the overall budget. Proper training is essential for ensuring that employees can effectively use the CRM software to its full potential. Here are some key points to consider:
Costs associated with training and onboarding
- Cost of training materials and resources, such as manuals, online courses, and training sessions.
- Cost of hiring external trainers or consultants to assist with the training process.
- Cost of employee time spent in training sessions, which can impact productivity.
- Cost of onboarding new employees onto the CRM software, including initial setup and training.
Best practices for minimizing training and onboarding expenses
- Utilize online training resources and self-paced learning modules to reduce the need for in-person training sessions.
- Implement a train-the-trainer approach where internal employees are trained to become CRM software experts and can then train their colleagues.
- Create detailed user guides and manuals to reduce the reliance on external trainers and consultants.
- Provide ongoing support and refresher training to ensure that employees continue to use the CRM software effectively.
Investing in training for cost savings and improved utilization
Proper training can lead to increased efficiency, reduced errors, and improved customer satisfaction, ultimately resulting in cost savings for the organization. Employees who are well-trained on CRM software are more likely to utilize its full potential, maximizing the return on investment.
Regulatory compliance costs in CRM software
In the realm of CRM software, regulatory compliance is a critical aspect that can significantly impact the overall cost of implementation and maintenance. Let’s delve into how regulatory requirements affect the expenses associated with CRM software solutions.
Impact of Regulatory Requirements
- Companies operating in industries such as healthcare, finance, and telecommunications are subject to stringent regulatory standards like HIPAA, GDPR, and PCI DSS. Ensuring compliance with these regulations often involves additional customization, security measures, and ongoing monitoring, leading to higher CRM software costs.
Financial Implications of Compliance
- Non-compliance penalties can result in hefty fines, legal fees, and damage to the organization’s reputation. Investing in robust compliance measures within CRM software may involve upfront costs but can save businesses from substantial financial losses in the long run.
Cost-Benefit Analysis for Compliance
- Organizations need to weigh the expenses of regulatory compliance against the potential risks of non-compliance. Conducting a cost-benefit analysis helps in determining the optimal level of investment required to meet regulatory standards while maximizing operational efficiency and mitigating financial liabilities.
Size of Organization and Compliance Costs
- Smaller businesses may find it challenging to allocate resources for comprehensive regulatory compliance compared to larger enterprises with dedicated compliance teams and budgets. The scale of operations and data handling directly influence the variations in CRM software costs related to regulatory compliance.
Data Security Measures and Expenses
- Implementing stringent data security measures, encryption protocols, and access controls to comply with regulations like GDPR or CCPA can elevate the costs associated with CRM software. Regular audits, vulnerability assessments, and data protection mechanisms contribute to ensuring compliance but also incur additional expenses.
Importance of Updates and Maintenance
- Regulatory requirements are subject to frequent updates and revisions, necessitating continuous monitoring and adjustments in CRM software. Investing in regular updates, patches, and maintenance services is crucial to stay compliant with evolving regulations and minimize the long-term costs of non-compliance penalties.
Case studies on successful CRM software cost management
Implementing CRM software can be a significant investment for businesses, but effective cost management strategies can lead to long-term savings and increased efficiency. Let’s explore some case studies of companies that have successfully managed their CRM software costs.
Company A: Optimizing CRM Software Costs
- Company A implemented a cloud-based CRM solution, reducing infrastructure costs and maintenance expenses significantly.
- They focused on regular monitoring and evaluation to identify areas for cost optimization and efficiency improvements.
- By utilizing a subscription-based pricing model, they were able to scale their CRM software usage according to their needs, avoiding unnecessary expenses.
- Initial investment: $50,000 | Long-term cost savings: Reduced maintenance costs by 30% annually
Company B: Cost Savings through Customization
- Company B opted for a CRM software with extensive customization options, tailored to their specific business requirements.
- They avoided unnecessary features and modules, focusing only on functionalities that added value to their operations.
- Through effective customization, they were able to streamline processes and reduce training expenses for employees.
- Initial investment: $80,000 | Long-term cost savings: 20% reduction in training and onboarding costs
Company C: Strategic Pricing Model Selection
- Company C carefully evaluated different CRM software pricing models and chose a per-user subscription plan that aligned with their budget and scalability needs.
- They negotiated pricing based on the number of users and features required, ensuring cost-effectiveness without compromising functionality.
- By leveraging volume discounts and flexible payment options, they achieved significant cost savings over time.
- Initial investment: $100,000 | Long-term cost savings: 25% reduction in CRM software expenses
Future trends in CRM software pricing
As technology continues to evolve and market dynamics shift, the pricing of CRM software is also expected to undergo changes in the future. Businesses need to anticipate these trends to optimize their software costs effectively.
Subscription-based Pricing Models
- Subscription-based pricing models are likely to become more prevalent in the future, offering businesses flexibility in payment options and scalability based on their needs.
- These models may include tiered pricing structures, where businesses can choose features and functionalities based on their budget and requirements.
- Businesses should assess the long-term costs of subscription-based models versus one-time payments to determine the most cost-effective option.
AI Integration and Personalization
- Advancements in artificial intelligence (AI) are expected to drive CRM software pricing, with AI-powered features becoming more prominent and adding value to businesses.
- Personalization capabilities within CRM software, driven by AI, may impact pricing as businesses seek more customized solutions to meet their unique needs.
- Businesses should evaluate the ROI of AI integration in CRM software to determine the cost-benefit ratio and competitive advantage.
Market Competition and Price Wars
- Increased competition among CRM software providers may lead to price wars in the market, offering businesses opportunities for cost savings and negotiation leverage.
- Businesses need to stay updated on market trends and competitor pricing strategies to make informed decisions and maximize cost savings.
- Strategic partnerships and vendor negotiations may play a crucial role in securing favorable pricing terms amidst market competition.
Final Conclusion
Explore the intricacies of CRM software cost and learn how to make informed decisions to maximize ROI and efficiency in your business operations.